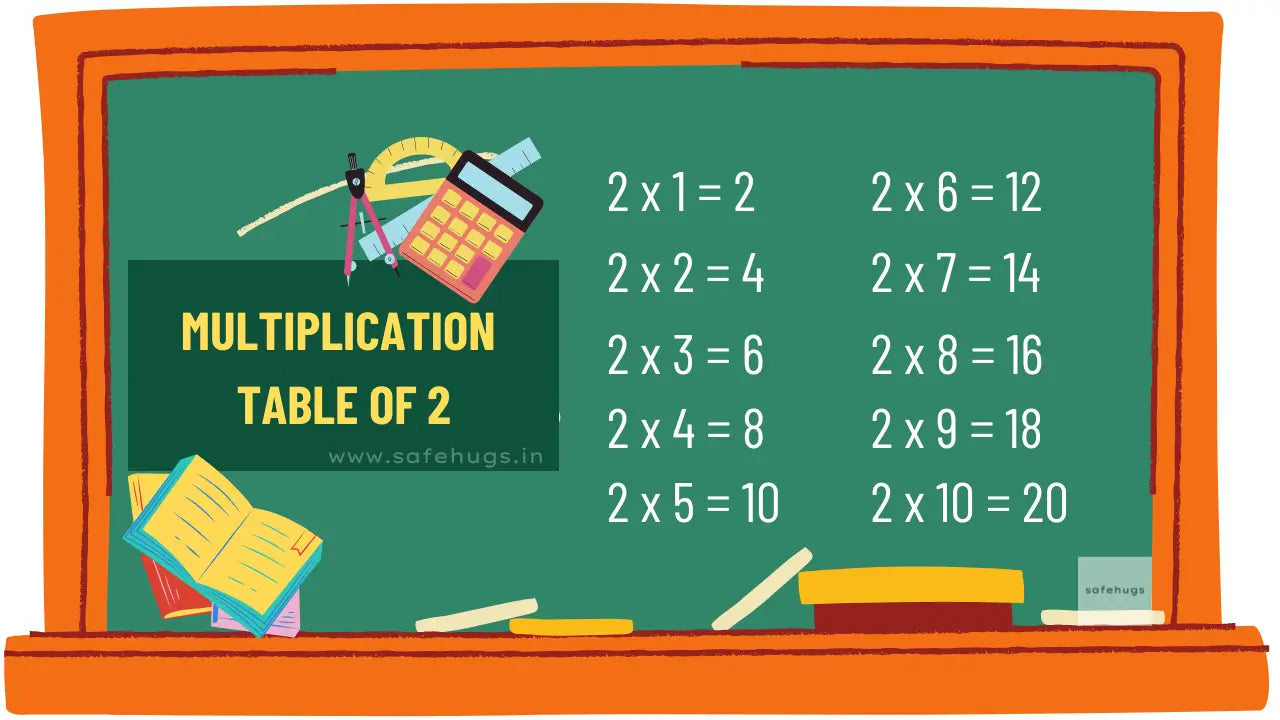
2 to 20 Tables: Multiplication Table For Kids
Multiplication tables from 2 to 20 are a fundamental part of math education, providing the building blocks for more advanced mathematical concepts. Mastering these tables not only enhances mental math skills but also boosts confidence in solving everyday math problems quickly and efficiently. Whether calculating totals, grouping items, or tackling schoolwork, a strong grasp of multiplication helps simplify a wide range of tasks. By learning the tables from 2 to 20, students set the stage for tackling more complex topics like division, fractions, and algebra, making it a vital step in their math journey.
Table of Contents
- Importance of Memorizing Tables
-
Detailed Tables Breakdown
- Tables 2 - 5
- Tables 6 - 10
- Tables 11 - 20
-
Practice Resources
- Quiz to Practice
- Worksheets
- YouTube
- 2 to 20 Tables Chart
- Link to Other Tables
- FAQ's
Importance of Memorizing Tables
Memorizing multiplication tables is crucial for several reasons:
- Foundation for Advanced Math: A solid understanding of multiplication tables lays the groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts, such as division, fractions, and algebra. This foundational knowledge is essential as students progress through their education.
- Enhanced Mental Math Skills: Memorizing tables improve mental math abilities, allowing individuals to perform calculations quickly and accurately without relying on calculators. This skill is invaluable in everyday situations, such as budgeting, shopping, or estimating costs.
- Increased Confidence: Mastery of multiplication tables boosts students’ confidence in their math skills. When they can recall these tables easily, they feel more competent in tackling math problems, which can lead to greater participation and success in math-related activities.
- Problem-Solving Efficiency: Knowing multiplication tables enables quicker problem-solving, especially in real-life scenarios that require rapid calculations, such as determining totals, dividing items into groups, or solving word problems in school.
- Building Critical Thinking: Understanding multiplication helps students recognize patterns and relationships between numbers, fostering critical thinking skills that are applicable in various areas of math and science.
- Long-Term Academic Success: Students who have a strong grasp of multiplication tables tend to perform better in math overall, leading to greater academic success and a stronger foundation for future learning in subjects that rely on math skills.
Detailed Tables Breakdown
Tables 2-5
| 2 Table |
Double It :Multiplying by 2 is the same as adding the number to itself (e.g., 2 × 7 is 7 + 7 = 14). Even Numbers: All results are even, making it easier to recognize mistakes. |
| 3 Table |
Add the Number Thrice: Visualize adding the number three times. Sum of Digits: For many results, the sum of the digits is divisible by 3.(e.g., 3 × 5 = 15, and 1 + 5 = 6, which is divisible by 3). |
| 4 Table |
Double the Doubles: Think of multiplying by 4 as doubling the number twice. (e.g., 4 × 5 is 5 + 5 = 10, then 10 + 10 = 20). Even Results: Similar to the 2 table, all results are even. |
| 5 Table |
Half of 10s: Multiplying by 5 is half of multiplying by 10. Alternating Pattern: Products end in 0 or 5, making it easy to check your answers (e.g., 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, etc.). |
General Tips For 2 to 5 Tables
- Finger Counting: For smaller tables like 2 and 3, using fingers can help younger learners.
- Songs and Rhymes: Rhythmic repetition through songs can reinforce memorization.


Click On Any Table To Download
Tables 6-10
|
6 Table
|
Double, Then Multiply by 3: Think of 6 as 2 × 3, so you can first double the number and then multiply by 3 Even Number Pattern: All results in the 6 times table are even |
| 7 Table |
Breakdown Method: Split the multiplication into easier parts Recognize Patterns: While the pattern could be more obvious, practicing through repeated counting (7, 14, 21, 28, etc.) helps. |
| 8 Table |
Double, Double, Double: Multiplying by 8 is like doubling a number three times Last Digit Pattern: The last digits repeat in a pattern: 8, 6, 4, 2, 0. |
| 9 Table |
Finger Trick: Hold your hands in front of you, palms down. For 9 × 3, fold down your third finger. The number of fingers to the left of the folded finger represents tens (2), and the right represents ones (7). So, 9 × 3 = 27. Digit Sum Equals 9: The sum of the digits in each product is always 9 (e.g., 9 × 4 = 36; 3 + 6 = 9). Decrease and Increase: For each step up (e.g., 9 × 1, 9 × 2, etc.), the tens digit increases by 1 and the ones digit decreases by 1 (09, 18, 27, 36, etc.). |
| 10 Table |
Add a Zero: Multiplying by 10 is straightforward—just add a zero to the end of the number (e.g., 10 × 6 = 60). Consistent Pattern: The results always end in 0, making them easy to remember. |
Click On Any Table To Download


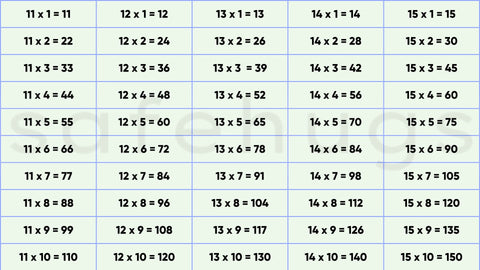
Tables 11-20
| 11 Table |
Repeat the Number:For 1-digit numbers, simply repeat the digit (e.g., 11 × 3 = 33, 11 × 4 = 44).
Two-Digit Trick: For 2-digit numbers, add the digits and place the sum between them (e.g., 11 × 12: 1 (1+2) 2 = 132). |
| 12 Table | Double the 6 Table: Double the products of the 6 table (e.g., 12 × 3 is double 6 × 3, so 18 × 2 = 36). |
| 14 Table |
Double the 7 Table: Multiplying by 14 is the same as doubling the 7 table (e.g., 14 × 4 = 7 × 4 × 2 = 28 × 2 = 56). |
| 15 Table |
Think of Multiples of 5: The results end in either 0 or 5 |
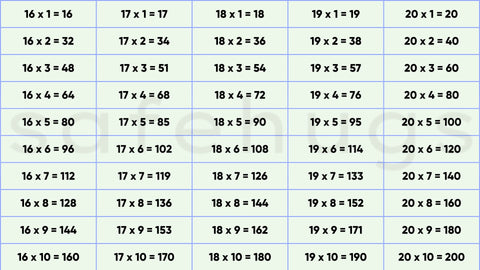
| 16 Table |
Double the 8 Table: Multiplying by 16 is like doubling the 8 table |
| 18 Table |
Double the 9 Table: Multiply by 9, then double the result (e.g., 18 × 4 = 9 × 4 × 2 = 36 × 2 = 72). |
| 19 Table |
Break into 20 and Subtract 1: 19 × n = (20 × n) − n (e.g., 19 × 4 = 80 − 4 = 76). |
| 20 Table |
Double the 10 Table: 20 × n is just double the result of 10 × n Add a Zero, Then Double: Like the 10 table, but double it (e.g., 20 × 4 = 80). |
Break into 10 and the number (n) Use 18 × n = (10 × n) + (8 × n)
Click On Any Table To Download


Practice Resources and Tools
Quiz to Practice 2 to 20 Tables




Worksheets
Here are some simple worksheets for kids to practice multiplication:
-
Multiplication Facts Worksheets: Practice basic multiplication problems like 2 × 3, 5 × 4, etc.
-
Multiplication Practice Worksheets: Mix up different multiplication problems for more practice.
-
Basic Multiplication Worksheets: Start with easy problems and work up to harder ones.
-
Multiplication Flashcards: Use cards with problems on one side and answers on the other for quick review.
These worksheets help kids learn multiplication tables in a fun and easy way.
YouTube
Here are some YouTube videos for kids to learn multiplication tables:
-
Multiplication Tables 1 - 20: Covers all tables from 1 to 20.
-
Learn Tables in Easy Way: Simple and fun way to learn tables.
-
Multiplication Tables For Children: Kid-friendly with visuals and songs.
-
2 to 20 Multiplication Tricks For Kids: Quick tricks to learn tables fast.
-
Learning Multiplication Tables: Step-by-step guide for learning tables.
-
Times Tables Easy Learn: Fun and easy way to learn times tables.
These videos make learning multiplication fun and easy!
2 to 20 Tables Chart

FAQ'S
1.Why is learning multiplication tables (2 to 20) important?
Mastering multiplication tables from 2 to 20 strengthens mental math skills, allowing for quicker and more efficient calculations. This foundational knowledge is essential for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts like division, fractions, and algebra.
2. What are some tips for memorizing multiplication tables (2 to 20)?
Break the tables down into manageable sections, use patterns (such as doubling for the 2 table or adding the base number repeatedly), practice with flashcards, and engage in fun quizzes or games. Writing the tables out several times also reinforces memory through repetition.
3. How can multiplication tables (2 to 20) be used in real life?
Multiplication tables are incredibly useful for daily tasks like grouping items, calculating costs, or solving math problems quickly. For example, knowing the tables can help when calculating the total cost of items priced in multiples or when organizing things in groups.
4. At what age should kids start learning multiplication tables (2 to 20)?
Children can begin learning smaller tables (such as 2 to 5) around ages 6 to 7 and gradually move to higher tables as they progress, typically by ages 8 to 10. This step-by-step approach prepares them for tackling more complex math problems in later grades.
5. Are there any tricks for quickly finding multiples for tables (2 to 20)?
Yes! One simple trick is to add the base number repeatedly to get the next multiple. For instance, for the 3 table, start with 3, add 3 to get 6, then 9, 12, and so forth. For larger tables like the 12 or 15 table, you can break them down by adding smaller known results (e.g., 10 + 2 for the 12 table). This method helps build the table step by step while reinforcing number patterns.