Understanding ADHD: Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. Despite its prevalence, there are many misconceptions surrounding ADHD that can lead to stigma and misunderstanding. In this blog, we will explore the myths and realities of ADHD, as well as provide insights into how individuals with ADHD can be supported.
What is ADHD?
ADHD stands for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. It's a neurodevelopmental disorder that can impact one's ability to focus, control impulses, and manage behaviours. People with ADHD may have difficulty paying attention, staying organized, and controlling their impulses, which can affect their daily functioning in various settings, including school, work, and relationships. ADHD is typically diagnosed in childhood, but symptoms can persist into adulthood.
Myths related to ADHD
Myth #1: ADHD is not a real disorder.
Reality: ADHD is a legitimate medical condition that affects the brain's functioning and development. Research has shown that individuals with ADHD have differences in brain structure and function, particularly in areas related to attention, impulse control, and executive functioning.
Myth #2: ADHD only affects children.
Reality: While ADHD is often diagnosed in childhood, it can persist into adolescence and adulthood. Many adults with ADHD were not diagnosed in childhood, leading to challenges in various areas of life, including work, relationships, and self-esteem.
Myth #3: People with ADHD are just lazy or lack discipline.
Reality: ADHD is not a result of laziness or a lack of discipline. It is a neurobiological condition that impacts a person's ability to regulate their attention, impulses, and activity levels. Individuals with ADHD often face challenges with organisation, time management, and completing tasks, despite their best efforts.
Myth #4: Medication is the only treatment for ADHD.
Reality: While medication can be a helpful tool in managing ADHD symptoms, it is not the only treatment option. Behavioural therapies, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and behaviour modification techniques, can also be effective in helping individuals with ADHD improve their focus, organisation, and self-control.
Myth #5: People with ADHD cannot succeed in life.
Reality: With the right support and accommodations, individuals with ADHD can lead successful and fulfilling lives. Many successful individuals, including entrepreneurs, artists, and athletes, have ADHD. By leveraging their strengths, such as creativity, energy, and resilience, individuals with ADHD can achieve their goals and excel in their chosen fields
ADHD Symptoms

ADHD is characterised by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can affect various aspects of life. Individuals with ADHD may struggle with:
- Inattention: Difficulty focusing on tasks, organising activities, and following through on instructions. Individuals with ADHD may seem careless or forgetful in daily activities.
- Hyperactivity: Restlessness, fidgeting, and difficulty staying seated in situations where it is expected.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, interrupting others, and engaging in risky behaviours without considering the consequences.
To know more about ADHD symptoms in toddlers, children, adolescents and adults.
Root Causes of ADHD

Research has shown that ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the brain's functioning and development. Here, we'll explore the potential causes and contributing factors of ADHD:
-
Genetic Influences: One of the strongest indicators of ADHD is its heritability. Studies have shown that ADHD tends to run in families, with genetics playing a significant role in its development. It is estimated that genetics account for approximately 74% of the risk for ADHD. Specific genes related to dopamine regulation, a neurotransmitter involved in attention and impulse control, have been implicated in ADHD.
- Neurobiological Basis: Brain imaging studies have revealed differences in the brains of individuals with ADHD compared to those without the disorder. These differences primarily involve areas of the brain responsible for attention, impulse control, and executive functioning. Reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex, which plays a crucial role in regulating attention and behaviour, has been observed in individuals with ADHD.
- Environmental Influences: While genetics play a significant role, environmental factors can also contribute to the development of ADHD. Factors such as exposure to toxins during pregnancy, premature birth, low birth weight, and early childhood trauma have been associated with an increased risk of developing ADHD.
RELATED: ADHD causes.
Effective Treatments for ADHD

While there is no one-size-fits-all treatment for ADHD, there are several effective strategies that can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Here's a concise overview:
- Medication: Stimulants like Ritalin can improve focus. Non-stimulants like Strattera are options too.
-
Therapy: Behavioural therapies like CBT can help develop coping strategies. Parent training is useful for caregivers.
"A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry found that children with ADHD who received behavioural therapy in addition to medication showed greater improvements in their symptoms compared to those who only received medication." - Lifestyle Changes: Structured routines, exercise, a healthy diet, and enough sleep can improve focus and reduce impulsivity.
- Support and Education: Joining support groups and educating others about ADHD can create a supportive environment.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation: Practices like meditation and yoga can reduce stress and improve attention.
By combining these approaches, individuals with ADHD can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
RELATED: Strategies for managing symptoms and finding support.
Other concerns and conditions

- Behaviour Problems in ADHD: Behaviour problems are common in individuals with ADHD, particularly in children. These problems can include oppositional behaviour, defiance, and aggression.
- Anxiety and Depression in ADHD: Anxiety and depression are also common in individuals with ADHD, both children and adults. The challenges of managing ADHD symptoms, such as difficulty focusing, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, can contribute to feelings of anxiety and depression.
- Learning Disabilities: Many individuals with ADHD also have learning disabilities, such as dyslexia or dyscalculia, which can impact their academic performance and require additional support and accommodations. "Since my ADHD diagnosis and treatment, my life has changed dramatically. I used to struggle with simple tasks and felt overwhelmed constantly. Now, with the right medication and therapy, I can focus better and manage my time effectively." - John Doe
- Sleep Problems: ADHD is often associated with sleep disturbances, including difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and waking up in the morning. Addressing sleep issues can help improve overall well-being and ADHD symptoms.
- Substance Abuse: Adolescents and adults with ADHD are at a higher risk of developing substance abuse issues, possibly due to impulsivity and sensation-seeking behaviour. It's essential to monitor for signs of substance abuse and seek help if needed.
-
Emotional Dysregulation: ADHD can contribute to difficulties in regulating emotions, leading to mood swings, irritability, and emotional outbursts. Learning coping strategies and emotional regulation skills can be beneficial.
- Relationship Problems: Adults with ADHD may experience challenges in maintaining relationships due to difficulties with communication, impulsivity, and forgetfulness. Relationship counselling can be helpful in improving communication and understanding.
- Employment Challenges: Adults with ADHD may face difficulties in the workplace, such as trouble meeting deadlines, staying organised, and maintaining focus. Workplace accommodations and strategies can help mitigate these challenges.
- Low Self-Esteem: ADHD symptoms can impact self-esteem, leading to feelings of inadequacy or failure. Building self-confidence and recognizing strengths can help improve self-esteem.
ADHD vs ADD
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) and ADD (Attention Deficit Disorder) are related terms that are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to slightly different presentations of the same disorder.
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder):
- ADHD is the official term used in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) to describe the disorder.
ADD (Attention Deficit Disorder):
- ADD is an outdated term that was used in older versions of the DSM to describe a subtype of ADHD characterised by primarily inattentive symptoms.
In summary, ADHD is the current term used to describe the disorder, and it encompasses both the inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive subtypes. The term ADD is no longer used in clinical practice, but it is sometimes used informally to refer to the inattentive subtype of ADHD.
To know more about the difference between ADHD and ADD.
ADHD VS SCHIZOPHRENIA
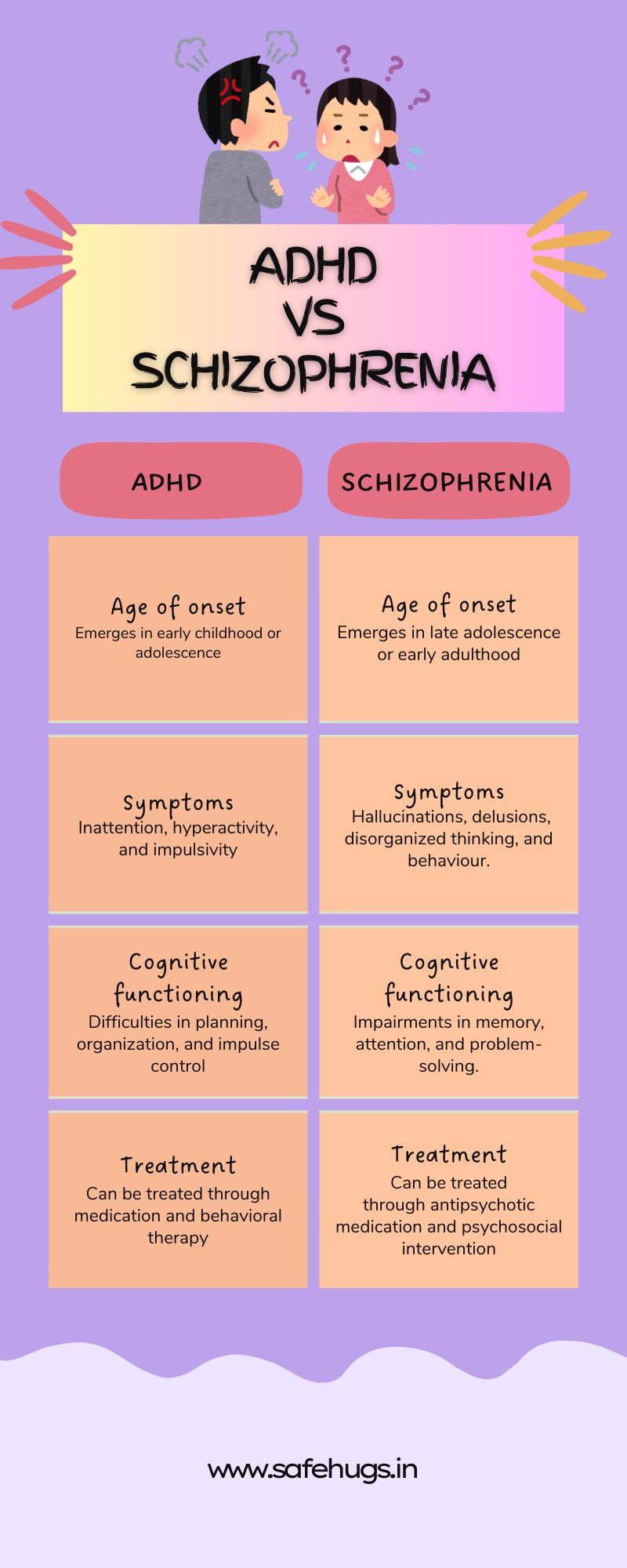
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) and schizophrenia are two distinct psychiatric disorders with different characteristics, though they can sometimes be confused due to overlapping symptoms. Here are the key differences between ADHD and schizophrenia:
- Age of Onset: ADHD typically presents in childhood and is often diagnosed in early childhood or adolescence. In contrast, schizophrenia usually emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood, although early-onset schizophrenia can occur in childhood or adolescence.
-
Symptoms: ADHD is characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms are chronic and persistent, often affecting various aspects of life, including school, work, and relationships. Schizophrenia is characterised by symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, disorganised thinking, and behaviour. While some symptoms may overlap with ADHD (e.g., attention difficulties), the nature and severity of these symptoms differ.
- Neurobiological Factors: Both disorders are believed to involve abnormalities in neurotransmitter systems, particularly dopamine. However, the specific neurobiological mechanisms and brain regions affected differ between ADHD and schizophrenia.
- Cognitive Functioning: Individuals with ADHD may have difficulties with executive functions such as planning, organisation, and impulse control. In schizophrenia, cognitive deficits are often more severe and can include impairments in memory, attention, and problem-solving.
- Treatment Approaches:
- ADHD: Treatment for ADHD often includes stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate or amphetamine, along with behavioral therapy and lifestyle modifications.
- Schizophrenia: Treatment for schizophrenia typically involves antipsychotic medications to manage psychotic symptoms, along with psychosocial interventions to support recovery and improve quality of life.
- Prognosis: While ADHD is a chronic condition, symptoms can often be managed effectively with treatment, and many individuals with ADHD lead successful lives. Schizophrenia is a more severe and disabling disorder, requiring ongoing treatment and support.
It's important to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of either disorder.
Tips for parenting
Parenting a child with ADHD can present unique challenges, but with patience, understanding, and a few strategies, you can help your child thrive. Here are some tips for parenting a child with ADHD:
- Learn About ADHD: Educate yourself about ADHD to better understand your child's challenges and strengths. Knowing what to expect can help you develop effective strategies for managing their behaviour. "As a parent of a child with ADHD, I was skeptical about medication at first. However, seeing the positive impact it has had on my child's behaviour and academic performance, I am grateful we decided to pursue treatment." - Jane Smith
- Establish Routines: Children with ADHD often benefit from structured routines. Establish daily routines for meals, homework, playtime, and bedtime to help your child know what to expect and reduce impulsivity.
- Set Clear Expectations: Be clear and consistent with your expectations. Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps and provide positive reinforcement for completing them.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Praise your child for their efforts and successes, no matter how small. Positive reinforcement can help motivate your child and build their self-esteem.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Use simple, direct language when giving instructions. Repeat instructions if necessary and provide visual cues or written lists to help your child remember tasks.
- Limit Distractions: Create a calm and organised environment at home. Minimise distractions during homework or tasks that require focus, such as turning off the TV or reducing background noise.
-
Encourage Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help improve focus and reduce hyperactivity. Encourage your child to engage in physical activities they enjoy, such as sports or dancing.

- Teach Coping Strategies: Help your child develop coping strategies for managing their ADHD symptoms, such as deep breathing exercises or taking short breaks when feeling overwhelmed.
- Work with School: Collaborate with your child's teachers and school to create a supportive learning environment. Share information about your child's ADHD and work together to implement strategies that can help them succeed in school.
- Seek Support: Connect with other parents of children with ADHD for support and advice. Consider joining a support group or seeking guidance from a mental health professional. "I am so inspired by the conversation, talking with people from all over the country with the same issues as me. I have felt like I was stuck on stupid for 50 years since I got my ADD diagnosis so late in life. After this call I feel not so alone." - Melanie, North Carolina
ADHD is a complex and often misunderstood disorder that can have a significant impact on individuals' lives. By debunking common myths and understanding the facts about ADHD, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for those affected by this condition. It's important to remember that ADHD is a medical condition that requires appropriate diagnosis and treatment. With the right support, individuals with ADHD can effectively manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Education and awareness are key to reducing stigma and ensuring that everyone affected by ADHD receives the support and understanding they deserve.





























