ADHD vs. ADD: Understanding the Differences
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) are two terms often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different subtypes of a similar condition. Understanding the distinction between ADHD and ADD can help individuals, parents, and professionals better recognize and address the specific challenges each presents. In this blog post, we aim to clarify the distinctions between ADHD and ADD, providing a comprehensive overview to aid in understanding and managing these conditions.
Table of Contents
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning or development. There are three subtypes of ADHD:
-
Predominantly Inattentive Presentation: Individuals with this subtype primarily exhibit symptoms of inattention. They may have difficulty sustaining attention, following through on tasks, and organising activities.
-
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation: This subtype is characterised by hyperactivity and impulsivity. Individuals may fidget, feel restless, interrupt others, and act without considering consequences.
- Combined Presentation: This is the most common subtype, where individuals exhibit both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms.
RELATED: ADHD Symptoms in Toddlers, Children, Adolescents and Adults.
What is ADD?
ADD was historically used to describe individuals who primarily had symptoms of inattention without the hyperactivity and impulsivity seen in ADHD. However, in current diagnostic criteria, ADD is considered a subtype of ADHD, specifically referring to the predominantly inattentive presentation.
ADHD vs. ADD: Understanding the Differences
Though ADHD and ADD are interchangeably used, they actually represent different aspects of the same condition. While both are subtypes of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, they manifest distinct symptom profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
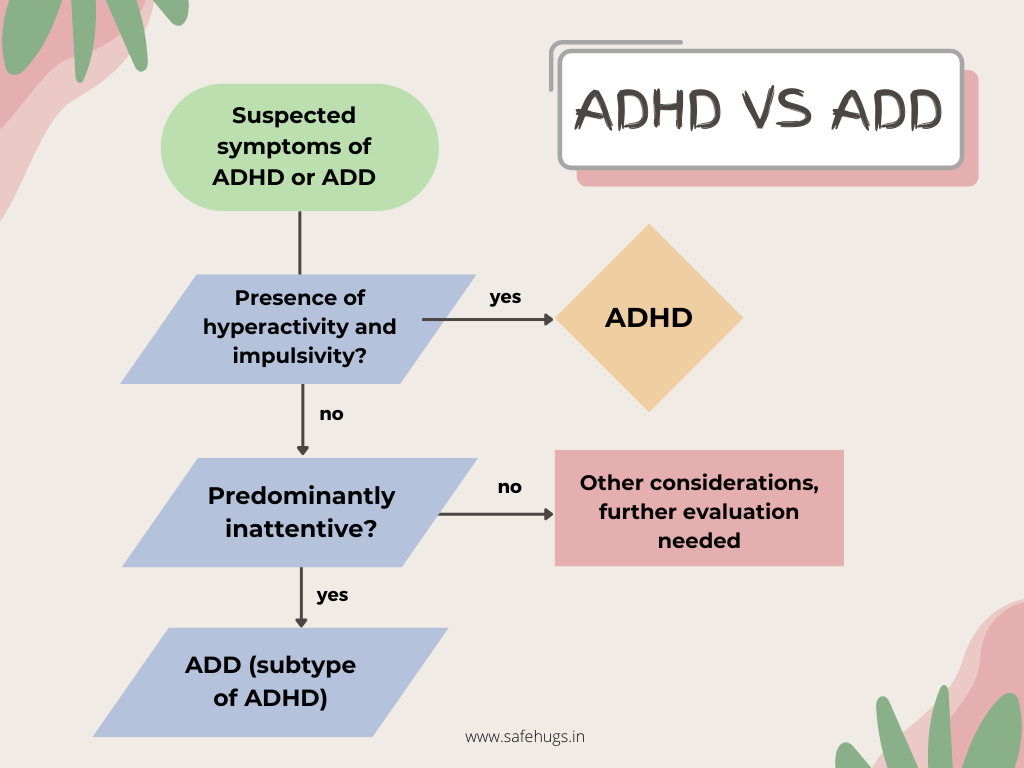
Key Differences between ADD and ADHD:
- Hyperactivity: ADHD includes hyperactive-impulsive symptoms, which are not present in ADD. This distinction is important as hyperactivity can significantly impact behaviour and social interactions.
-
Impulsivity: While individuals with ADD can be impulsive, it is a defining feature of the hyperactive-impulsive subtype of ADHD. Impulsivity can lead to difficulties in self-control and decision-making.
"As a parent, understanding the differences between ADHD and ADD has been crucial in helping my child receive the right support and treatment." - Parent of a child with ADHD
-
Diagnostic Criteria: The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) no longer recognizes ADD as a separate diagnosis. Instead, it categorises all presentations under the umbrella term ADHD, with different subtypes based on the predominant symptoms.
- Treatment Considerations: Treatment for both ADD and ADHD typically involves a combination of behavioural therapies, lifestyle modifications, and medication. However, the specific approach may vary based on the individual's subtype and symptoms.
Similarities Between ADHD and ADD
Both ADHD and ADD share core features such as difficulties with attention, organisation, and impulsivity. Individuals with either condition may struggle in academic, occupational, or social settings due to these symptoms. A study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry found that individuals with ADHD, particularly the hyperactive-impulsive subtype, often have more severe symptoms and functional impairments compared to those with ADD. Additionally, both conditions can co-occur with other mental health issues such as anxiety disorders or learning disabilities.

Treatment Options
Treatment for ADHD and ADD often involves a combination of medication, behavioural therapy, and educational support. Medications such as stimulants and non-stimulants can help manage symptoms, while behavioural interventions focus on developing coping strategies and improving organisation and time management skills.
|
Dr. Jane Smith, Clinical Psychologist: "Behavioural therapies, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy, can be highly effective in teaching individuals with ADHD or ADD coping strategies and improving their overall quality of life."
|
Misconceptions and Stigma
There are several misconceptions surrounding ADHD and ADD, including the belief that they are not real disorders or that they only affect children. It is important to recognize that these are legitimate neurodevelopmental disorders that can impact individuals of all ages. Addressing these misconceptions can help reduce the stigma associated with these conditions.
Living with ADHD or ADD
Managing ADHD or ADD involves developing strategies to cope with symptoms and improve daily functioning. This may include creating a structured routine, breaking tasks into smaller steps, and using tools such as planners or timers to stay organised. It is also essential for individuals with ADHD or ADD to seek support from healthcare professionals, educators, and loved ones.
In conclusion, ADHD and ADD are neurodevelopmental disorders that can significantly impact an individual's life. By understanding the differences and similarities between these conditions, we can better support those affected and work towards reducing stigma. Seeking professional help and implementing appropriate strategies can help individuals with ADHD or ADD lead fulfilling lives.






























